|
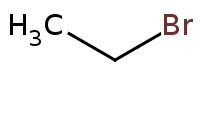



|
 |
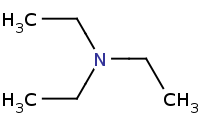

Warning: Amines (and ammonia) are good nucleophiles, but are not generally useful for preparing primary amines because of rampant over-alkylation.
|
|
|
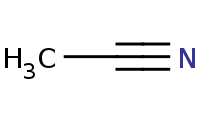

|
 |
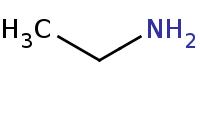

Note: Primary amines can be prepared by reduction of nitriles.
|
|
|
[O-]](https://re.edugen.wiley.com/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=c1ccc%28cc1%29%5BN%2B%5D%28%3DO%29%5BO-%5D&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)

|
 |


Note: Primary amines can be prepared by reduction of nitro groups.
|
|
|

|
 |
![c1ccc2c(c1)C(=NC2=O)[O-].[Na+]](https://re.edugen.wiley.com/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=c1ccc2c%28c1%29C%28%3DNC2%3DO%29%5BO-%5D.%5BNa%2B%5D&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)

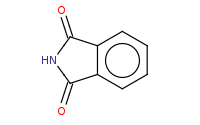
Note: Gabriel synthesis of primary amines starts with deprotonation of phthalimide to produce a good nucleophile.
|
|
|
![c1ccc2c(c1)C(=NC2=O)[O-].[Na+]](https://re.edugen.wiley.com/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=c1ccc2c%28c1%29C%28%3DNC2%3DO%29%5BO-%5D.%5BNa%2B%5D&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)



|
 |
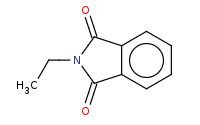

Note: Gabriel synthesis of primary amines includes a typical Sn2 reaction against an unhindered alkyl halide, using the deprotonated phthalimide as the nitrogen nucleophile. Note that further (over) alkylation is not a problem for this product.
|
|
|


|
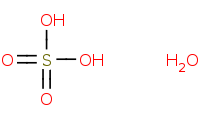
(hot, dilute)
 |


Note: The final step of Gabriel synthesis of a primary amine is hydrolysis of the phthalimide. This is comparable to hydrolysis of an amide to an amine and carboxylic acid.
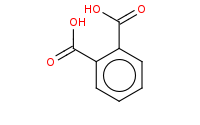

|
|
|

|
 |


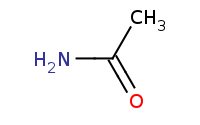
Note: Primary amides can be reduced to primary amines.
|
|
|

|
 |
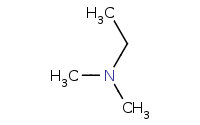

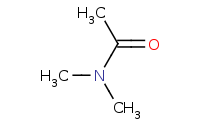
Note: Higher order amides can be reduced to form higher order amines.
|
|
|



|
 |


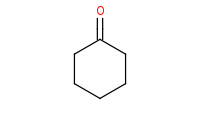
Note: Reductive amination couples amines and carbonyls (aldehydes and ketones). This is essentially a 2-step reaction with initial condensation of the amine and carbonyl to form an imine, which the reducing agent then converts into a secondary amine.
|
|
|




|
 |


Note: Reductive amination with a secondary amine yields a tertiary amine via an iminium ion intermediate.
|
|
|


|
 |
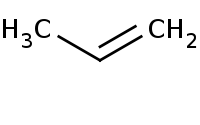

Note: Hofmann elimination of amines to alkenes. Refer to the [Mechanism] for more details on the initial 'exhaustive methylation' of the amine to form a decent leaving group out of a quarternary ammonium salt, followed by E2 elimination by hydroxide ion.
|
|
|
N](https://re.edugen.wiley.com/arrow-webapp/ArrowWebService?action=smi2png&smiles=CC%5BC%40H%5D%28C%29N&width=200&height=125&arrowdesc=&extraImageSetting=amap)

|
 |
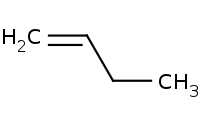

Note: Hofmann elimination is distinctive for producing the anti-Zaitsev product. In other words, it is regioselective to produce the least substituted alkene.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(0.111 sec)
Link
|
|